What methods are used to laminate or bond the layers of fabric together?
Several methods are used to laminate or bond the layers of fabric together in the production of
inflatable fabric. These methods ensure proper adhesion and bonding between the layers to create a strong and durable material suitable for inflatable structures. Some common methods include:
Heat Sealing:Heat sealing is a widely used method for bonding layers of fabric together in
PVC Inflatable Fabric production.
In this process, the edges of the fabric layers are overlapped, and heat is applied using a heated sealing bar or roller.
The heat melts the thermoplastic coating or adhesive on the fabric layers, creating a fusion bond between them as they cool and solidify.
Heat sealing is particularly suitable for joining thermoplastic materials such as PVC, TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane), or PU (polyurethane) coated fabrics.
High-Frequency Welding:High-frequency welding, also known as radio frequency (RF) welding, is another method used for bonding layers of fabric together.
In this process, an RF generator produces an electric field that causes polar molecules in the fabric to oscillate rapidly, generating heat.
The heated fabric layers are pressed together using a die or electrode, which applies pressure and fuses the layers together through molecular agitation and melting.
High-frequency welding creates strong, airtight seams and is often used for welding PVC or TPU-coated fabrics in the production of inflatable structures.
Ultrasonic Welding:Ultrasonic welding utilizes high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to bond thermoplastic materials together.
In this process, the fabric layers are placed between a vibrating ultrasonic horn and an anvil, which apply pressure and ultrasonic energy to the material.
The ultrasonic energy causes frictional heating at the interface of the fabric layers, melting the thermoplastic coating and creating a molecular bond as the layers cool.
Ultrasonic welding is fast, precise, and suitable for joining thin or delicate fabrics, but it may have limitations in bonding thicker or heavier materials.
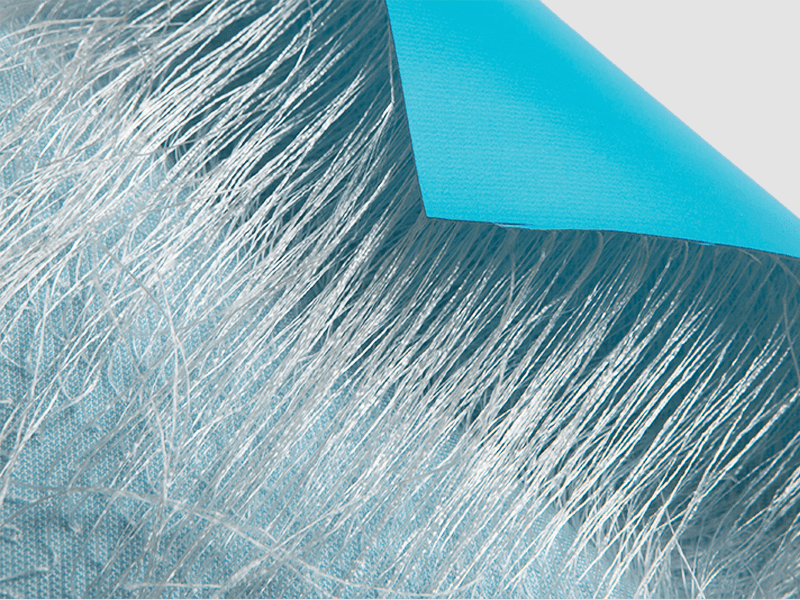
Adhesive Bonding:Adhesive bonding involves applying a layer of adhesive or bonding agent between the fabric layers to create a strong bond.
The adhesive is typically applied in liquid or film form and is activated by heat, pressure, or solvent evaporation.
Once the adhesive is applied, the fabric layers are pressed together and allowed to cure or set, forming a durable bond.
Adhesive bonding can be used with a variety of fabric materials and is often used for bonding non-thermoplastic fabrics or materials with different properties.
Solvent Bonding:Solvent bonding involves applying a solvent or chemical adhesive to the fabric layers, which softens and dissolves the surface of the materials, creating a bond when pressed together.
The solvent evaporates, leaving behind a strong, permanent bond between the fabric layers.
Solvent bonding is suitable for joining materials such as PVC, PU, or TPU-coated fabrics and is often used in the production of inflatable structures.
These methods may vary depending on factors such as the type of fabric, coating materials, and intended application of the inflatable fabric. Each method has its advantages and limitations in terms of bonding strength, production efficiency, and suitability for specific materials and applications.
How does the choice of inflatable fabric type and seam construction affect the overall design and performance of inflatable structures?
The choice of
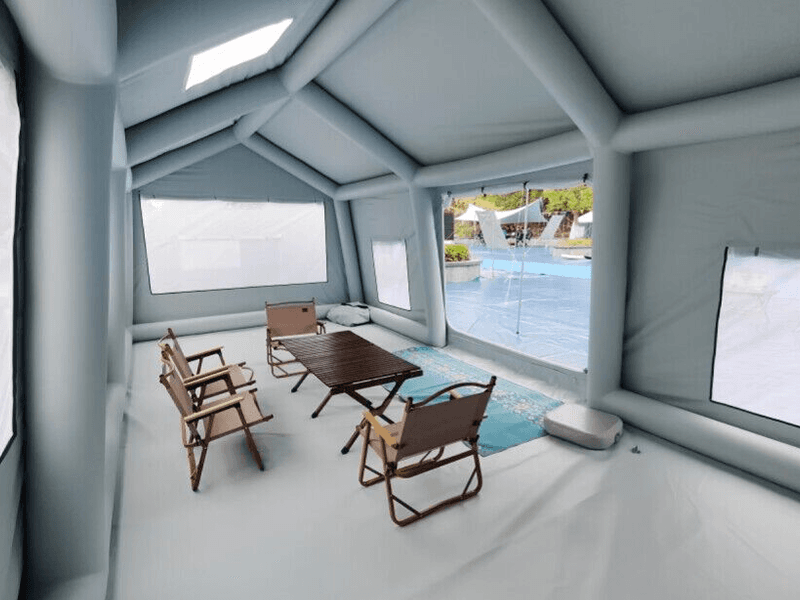
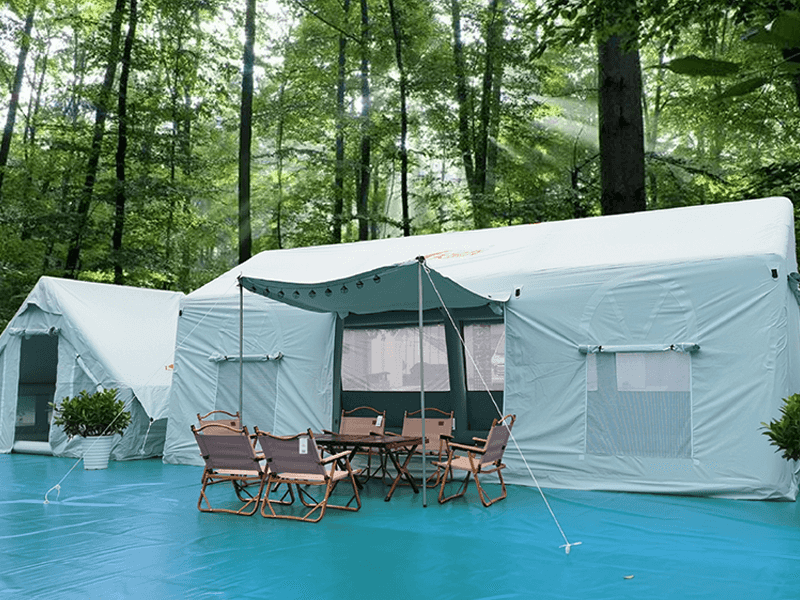
PVC Inflatable Material type and seam construction significantly impacts the overall design and performance of inflatable structures. Here's how each factor influences inflatable structure design and performance:
Inflatable Fabric Type:Material Properties: Different types of inflatable fabrics have unique properties that affect their suitability for specific applications. For example, PVC (polyvinyl chloride) coated fabrics are durable, waterproof, and resistant to UV degradation, making them suitable for outdoor use. TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) coated fabrics offer high tensile strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for rugged environments.
Weight and Thickness: The weight and thickness of the inflatable fabric impact the structural integrity, buoyancy, and handling characteristics of the inflatable structure. Lightweight fabrics are easier to transport and inflate but may sacrifice durability, while heavier fabrics offer greater strength and puncture resistance but may be more challenging to handle.
Flexibility and Stretch: The flexibility and stretch characteristics of the fabric influence its ability to conform to different shapes and withstand internal pressure changes during inflation and deflation. Fabrics with high flexibility and stretchability can accommodate complex designs and dynamic loads, enhancing the versatility and performance of inflatable structures.
Seam Construction:Seam Strength: The strength and integrity of seams are critical for maintaining the structural stability and airtightness of inflatable structures. Different seam construction techniques, such as heat sealing, high-frequency welding, or adhesive bonding, offer varying levels of seam strength and durability. Strong, airtight seams are essential for preventing air leaks, maintaining pressure stability, and ensuring the overall safety and performance of the inflatable structure.
Seam Placement and Design: The placement and design of seams impact the structural integrity and aesthetics of the inflatable structure. Strategic placement of seams along load-bearing areas and stress points helps distribute forces evenly and minimize the risk of seam failure or rupture. Seam design features, such as reinforcement patches, overlapping layers, and tapered edges, enhance seam strength and resistance to tearing, especially in high-stress areas.
Airtightness and Leak Prevention: Proper seam construction techniques are essential for achieving airtight seals and preventing air leakage in inflatable structures. Quality control measures, such as pressure testing, seam inspection, and leak detection, ensure that seams meet performance standards and maintain pressure integrity over time. Reliable seam construction is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and usability of inflatable structures in various environments and applications.

 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español