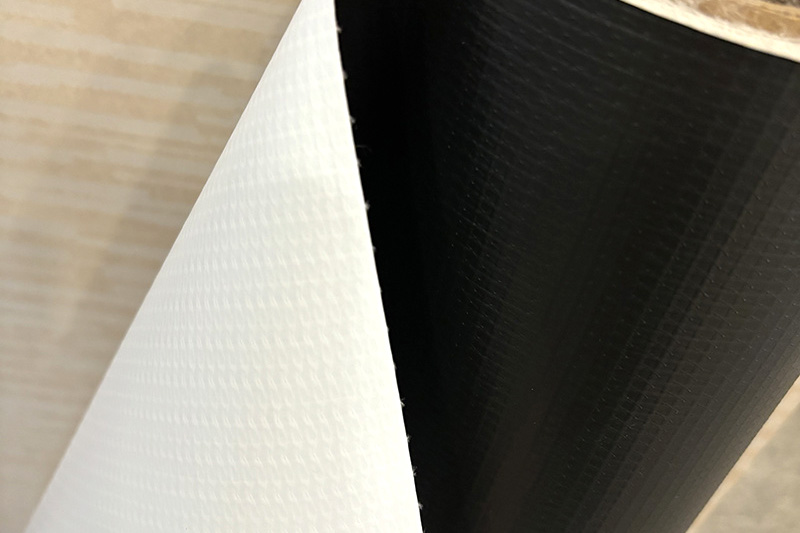
The flexibility and tensile strength of PVC Inflatable Fabric are important factors in its long-term stable use in various applications. To ensure these properties, manufacturers will optimize the elasticity and tensile strength of the fabric through careful material selection and production processes. The following are several key factors to ensure the flexibility and tensile strength of PVC inflatable fabric:
1. Selection of high-quality raw materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resin: The basis of PVC inflatable fabric is PVC resin, which has good flexibility and moderate hardness. By selecting high-quality PVC resin, the flexibility of the fabric can be improved, allowing it to remain elastic and adaptable in low temperature and high pressure environments.
Use of plasticizers: To improve the flexibility of PVC, manufacturers will add plasticizers (such as phthalates) during the production process. Plasticizers can reduce the hardness of PVC, making it softer, and enhance the ductility and tensile strength of the fabric, thereby ensuring that the inflatable fabric can maintain good flexibility during use.
2. Use of composite materials
High-strength fiber reinforcement layer: To improve the tensile strength of PVC inflatable fabric, many high-quality PVC inflatable fabrics use fiber reinforcement layers, such as polyester fibers or nylon fibers. These reinforcement layers can greatly improve the tensile strength and wear resistance of the fabric, making the fabric more durable and less likely to deform or break under high tensile forces.
Multi-layer structure design: Some PVC inflatable fabrics adopt a multi-layer structure, in which the outer layer is usually PVC material, and the middle layer may be a reinforced fiber or fabric layer. This multi-layer structure can effectively improve the tensile strength of the fabric while maintaining good flexibility.
3. High-temperature hot pressing process
Heat-sealing process: When manufacturing PVC inflatable fabrics, high-temperature heat-sealing technology is often used to process the seams of the fabric. Hot pressing technology can melt PVC at high temperature and make it tightly bonded with the fiber layer or other PVC layers, thereby increasing the tensile resistance and overall stability of the fabric.
Temperature control: Temperature control is very critical during the heat-sealing process. If the temperature is too high, the material may soften excessively, affecting flexibility; if the temperature is too low, the seams may be loose, affecting tensile resistance.
4. Surface coating and treatment
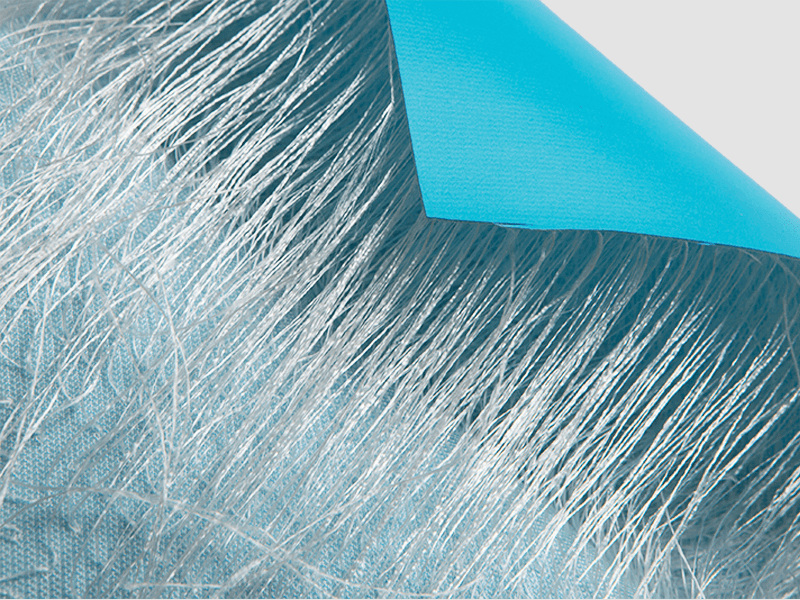

Stretch-resistant coating: Some PVC inflatable fabrics have a stretch-resistant coating applied to their surface, which can enhance the fabric's stretch resistance while improving its surface smoothness and abrasion resistance. Such coatings can prevent the fabric from surface damage caused by repeated stretching.
UV anti-ultraviolet treatment: In order to prevent the fabric from losing its elasticity and stretch resistance due to long-term exposure to sunlight, many PVC inflatable fabrics are also treated with UV anti-ultraviolet treatment. This treatment can prevent the fabric from aging under strong ultraviolet radiation and maintain its flexibility and stretch resistance.
5. Flexibility adjustment and thickness design
Optimization of fabric thickness: The thickness of PVC inflatable fabrics has an important impact on its flexibility and stretch resistance. Generally, thinner fabrics have better flexibility but may not be as stretch-resistant as thicker fabrics; while thicker fabrics can provide higher tensile strength. Depending on the needs of different applications, manufacturers will adjust the thickness of the fabric to balance flexibility and stretch resistance.
Flexibility adjustment: In some cases, manufacturers will further improve the flexibility of the fabric by adjusting the formula of PVC or adding other reinforcing materials. In this way, it can be ensured that the fabric can maintain the necessary flexibility after inflation and will not be damaged due to excessive stretching.
6. High and low temperature resistance
Temperature adaptability: The flexibility of PVC inflatable fabrics not only performs well at room temperature, but also needs to remain elastic under low and high temperature conditions. In a low temperature environment, PVC may become brittle, so manufacturers will choose a PVC formula suitable for low temperature use and add anti-low temperature agents when necessary to ensure that the fabric is still flexible enough in cold conditions.
High temperature adaptability: In a high temperature environment, PVC fabrics may become soft and affect their tensile strength. Therefore, by adjusting the type and content of plasticizers, it can be ensured that the fabric still maintains stable flexibility and tensile resistance at higher temperatures.
7. Quality control and testing
Tensile test: During the production process, manufacturers will conduct strict tensile tests on PVC inflatable fabrics. These tests include measuring the elongation, breaking strength and other performance indicators of the fabric under different tensile conditions to ensure that the fabric can maintain the required flexibility and tensile strength during actual use.
Quality inspection: In addition to tensile testing, manufacturers will also conduct other physical and chemical tests on PVC inflatable fabrics, such as wear resistance, aging resistance, UV resistance, etc., to ensure that the various properties of the fabric meet the requirements of use.
By selecting high-quality PVC resin, adding fiber reinforcement layers, using high-temperature heat-sealing processes, applying anti-stretch coatings and other methods, PVC inflatable fabrics can maintain flexibility while ensuring that they have strong tensile resistance. These measures can enable the fabric to maintain stable performance under different environmental conditions, such as temperature changes, long-term exposure, mechanical stretching, etc., and extend its service life.

 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español