What are the key physical and mechanical properties of Polyether TPU?
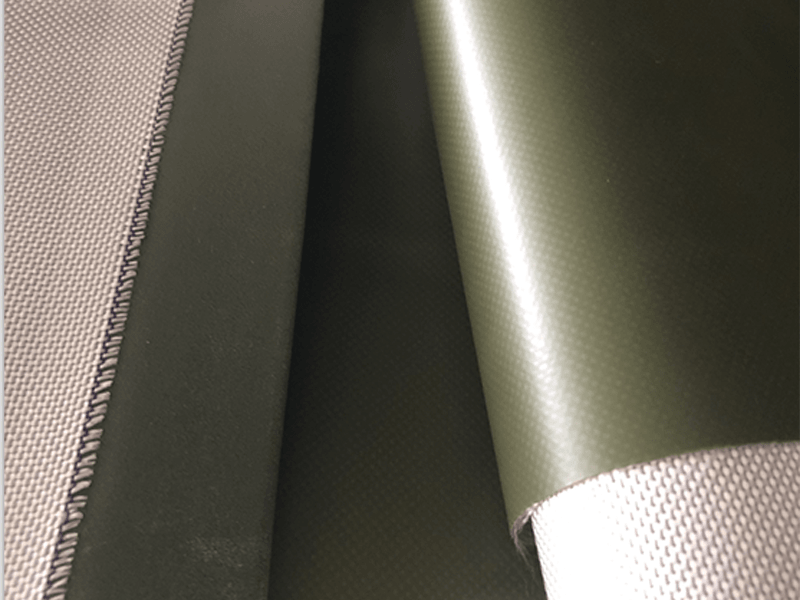
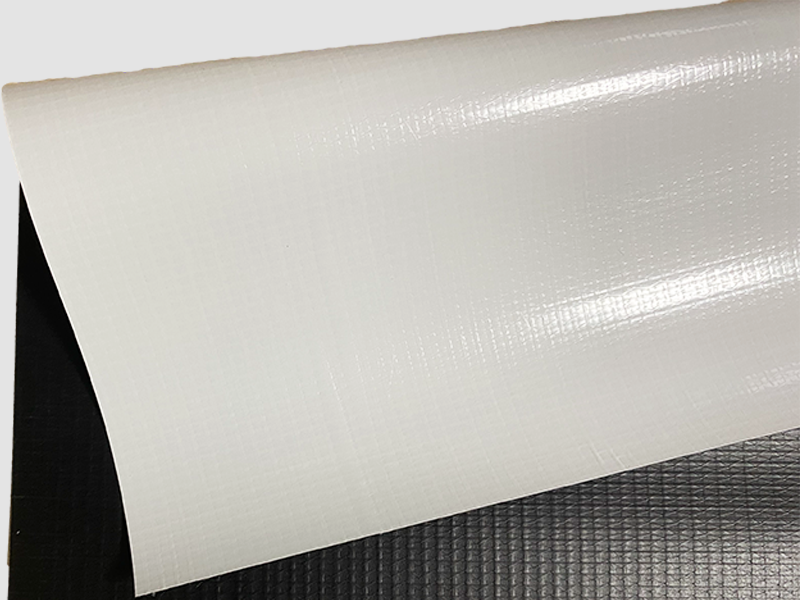
Polyether TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) exhibits a diverse range of physical and mechanical properties, making it suitable for a wide variety of applications across various industries. Here are some key properties of Polyether TPU:
Flexibility and Elongation:Polyether TPU is known for its exceptional flexibility and elongation properties, allowing it to stretch and recover without permanent deformation.
It can typically withstand elongation at break ranging from 400% to 700% or higher, depending on the specific formulation and processing conditions.
Tensile Strength:Polyether TPU exhibits high tensile strength, enabling it to resist pulling or stretching forces without tearing or breaking.
Tensile strength values for Polyether TPU can range from around 20 MPa to 60 MPa, depending on the grade and formulation.
Abrasion Resistance:Polyether TPU offers excellent abrasion resistance, making it suitable for applications subjected to wear and friction.
Its resistance to abrasion helps maintain its appearance and integrity over extended periods of use, even in harsh environments.
Tear Resistance:Polyether TPU demonstrates superior tear resistance, allowing it to withstand tearing forces without propagating or rupturing.
It can resist tear propagation under both static and dynamic loading conditions, contributing to its durability and longevity.
Chemical Resistance:Polyether TPU exhibits good resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including oils, greases, solvents, and fuels.
Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for applications where exposure to harsh substances is expected, such as automotive components, industrial seals, and medical devices.
Weather Resistance:Polyether TPU shows excellent weather resistance, withstanding exposure to sunlight (UV radiation), moisture, and temperature fluctuations.
It maintains its physical and mechanical properties over prolonged outdoor exposure, making it suitable for outdoor applications such as awnings, tents, and outdoor gear.
Softness and Shore Hardness:Polyether TPU can be formulated to exhibit a wide range of hardness levels, from very soft (Shore 40A or lower) to very hard (Shore 80A or higher).
Its softness or hardness can be tailored to specific application requirements, such as cushioning, impact absorption, or structural support.
Thermal Stability:Polyether TPU demonstrates good thermal stability, retaining its mechanical properties over a broad temperature range.
Can Polyether TPU be molded, extruded, or 3D printed?
Polyether TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) can be molded, extruded, and 3D printed, offering versatility in manufacturing processes to create a wide range of products with different shapes, sizes, and complexities. Here's how Polyether TPU can be used in each of these processes:
Molding:Polyether TPU is commonly used in injection molding and compression molding processes to produce parts and components with complex geometries and precise dimensions.
In injection molding, molten Polyether TPU is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure, where it solidifies and takes the shape of the mold.
Compression molding involves placing preheated Polyether TPU material into a heated mold cavity and applying pressure to compress and shape the material.
Molding is suitable for producing a wide range of Polyether TPU products, including automotive parts, footwear components, seals, gaskets, and medical devices.
Extrusion:Polyether TPU can be extruded into various forms, including sheets, films, tubes, profiles, and filaments, using extrusion processes such as flat die extrusion, blown film extrusion, and profile extrusion.
In flat die extrusion, molten Polyether TPU is forced through a flat die to form continuous sheets or films of uniform thickness.
Blown film extrusion involves extruding molten Polyether TPU through a circular die and inflating it with air to create thin-walled tubes or bubbles, which are then cooled and flattened into films.
Profile extrusion is used to produce Polyether TPU profiles with specific cross-sectional shapes, such as rods, channels, or tubing.
Extrusion is utilized in various industries for applications such as packaging films, protective coatings, wire and cable insulation, and medical tubing.
3D Printing:Polyether TPU is suitable for 3D printing (additive manufacturing) using selective laser sintering (SLS) or fused deposition modeling (FDM) techniques.
In SLS 3D printing, powdered Polyether TPU is selectively fused together layer by layer using a laser beam, resulting in parts with high accuracy and fine details.
FDM 3D printing involves extruding molten Polyether TPU filament through a heated nozzle onto a build platform, where it solidifies layer by layer to form the desired object.
3D printing with Polyether TPU offers advantages such as design flexibility, rapid prototyping, and customization, making it suitable for producing prototypes, tooling, orthopedic devices, and consumer products.

 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español