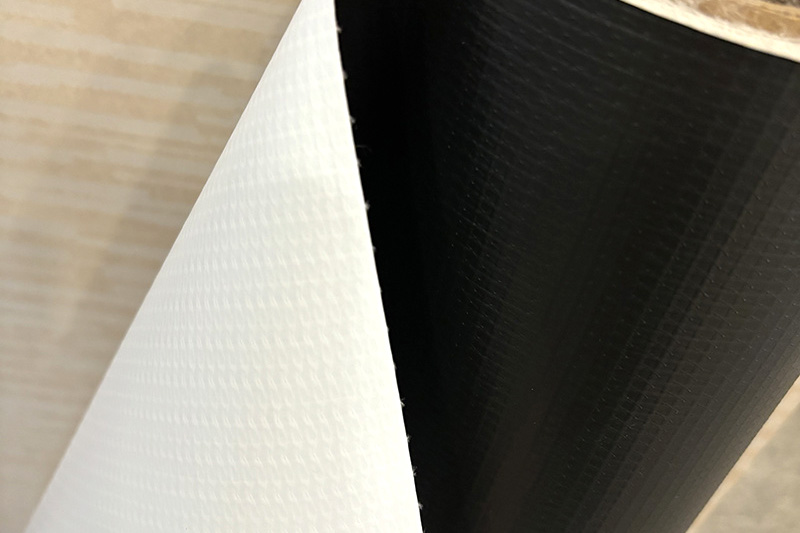
PVC inflatable fabric is widely used in a variety of applications—from inflatable pools and bounce houses to advertising balloons, temporary shelters, and water sports equipment. A common concern among consumers and commercial users is: How strong is it? The answer depends on the material composition, construction methods, and intended use. Below is a detailed, point-by-point analysis of the strength and durability of PVC inflatable fabric.
1. What Is PVC Inflatable Fabric?
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): A synthetic plastic polymer known for its durability, flexibility, and low cost.
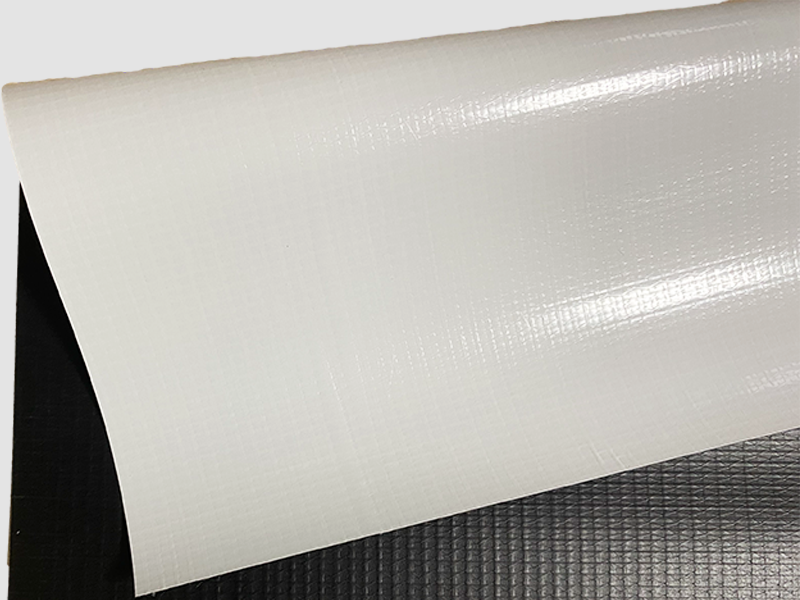
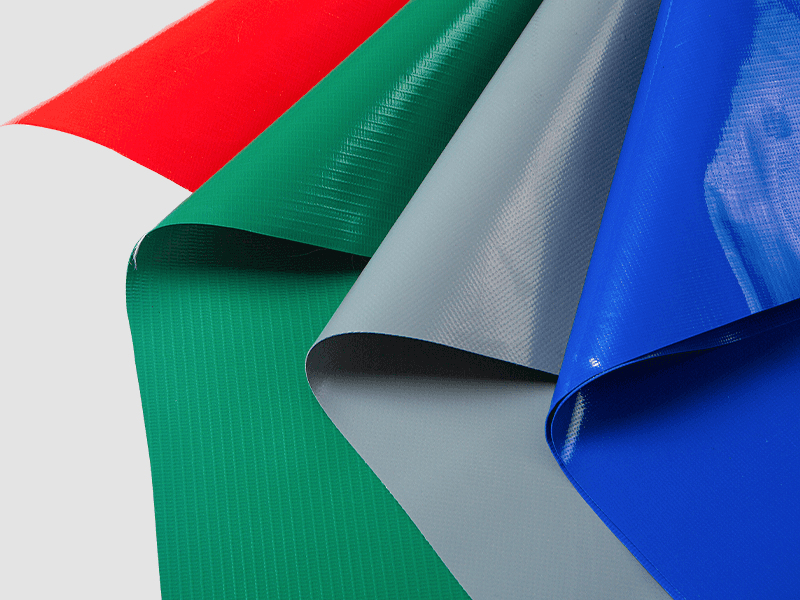
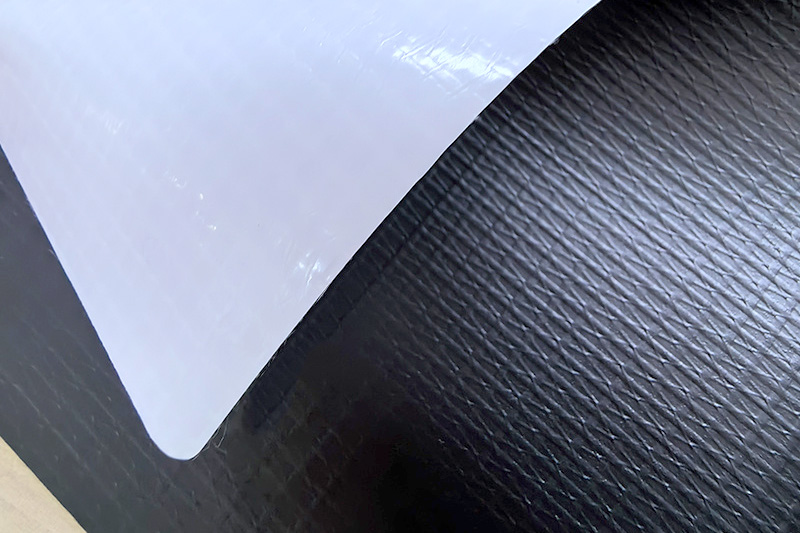
Inflatable Fabric: Typically consists of a woven polyester or nylon scrim sandwiched between two layers of PVC coating. This structure is called laminated PVC fabric or coated tarpaulin.
Common thicknesses range from 0.25 mm to 0.9 mm, with heavier-duty applications using thicker, reinforced materials.
The internal scrim (mesh) provides tensile strength, while the PVC coating ensures airtightness, waterproofing, and resistance to environmental damage.
2. Tensile and Tear Strength
High Tensile Strength: The embedded polyester or nylon scrim gives the fabric excellent resistance to stretching and pulling forces. For example, high-grade PVC inflatable fabric can have a tensile strength of over 100 N/25mm in both warp and weft directions.
Tear Resistance: Reinforced with scrim, the fabric resists small tears from spreading. Quality materials can withstand tear forces of 50–100 N or more, depending on thickness and weave density.
Burst Strength: Can handle internal air pressure from 0.3 to 1.0 psi (2–7 kPa), sufficient for most inflatable structures.
This makes PVC inflatable fabric strong enough to support heavy loads—such as children jumping on bounce houses or adults lying on inflatable rafts.
3. Puncture and Abrasion Resistance
Puncture Resistance: While not as tough as solid rubber or canvas, multi-layer PVC fabric resists punctures from sharp objects better than thin plastic films. Thicker versions (0.6–0.9 mm) are used in rugged environments like military shelters or industrial covers.
Abrasion Resistance: The PVC surface is smooth and durable, able to withstand friction from ground contact, sand, and repeated inflation/deflation. Some fabrics include anti-abrasion topcoats for extended life.
However, dragging on rough surfaces or exposure to sharp debris can still cause damage—proper use and care are essential.
4. Environmental Durability
UV Resistance: Most high-quality PVC inflatable fabrics are treated with UV inhibitors to prevent degradation from sunlight. They can last 3–5 years or more in outdoor conditions with proper maintenance.
Weather Resistance: Fully waterproof and functional in rain, snow,
and humidity. Performs well in temperatures from -10°C to +70°C (14°F to 158°F), though extreme cold can make the material brittle.
Mold and Mildew Resistance: PVC is inherently resistant, and many fabrics include anti-fungal additives to prevent growth in damp storage conditions.
These properties make PVC fabric strong not just mechanically, but also in long-term environmental performance.
5. Comparison with Other Inflatable Materials
vs. TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane):
TPU is more elastic and environmentally friendly, with better low-temperature flexibility and higher puncture resistance. However, it is significantly more expensive. PVC remains the preferred choice for cost-effective, strong inflatable products.
vs. Latex or Rubber Bladders:
Older inflatables used rubber, which is less durable and prone to cracking. PVC is far stronger and longer-lasting.
vs. Nylon or Polyester Alone:
Uncoated fabrics are not airtight. The PVC coating adds structural integrity and sealing capability, making the composite much stronger for inflation.
6. Real-World Applications Prove Strength
The strength of PVC inflatable fabric is demonstrated in demanding uses:
Inflatable Bounce Houses: Support repeated jumping by children, with walls and floors enduring constant stress.
Inflatable Boats (RIBs): Used in rescue operations and rough waters—require high burst and abrasion resistance.
Advertising Air Dancers: Stand tall in wind and weather, surviving outdoor exposure for months.
Temporary Shelters and Domes: Used in disaster relief and events—must resist wind loads and maintain shape.
Water Park Obstacles: Bear heavy user traffic and constant water exposure.
These applications would not be possible if the material were not structurally strong.
7. Limitations and Care Tips
Despite its strength, PVC inflatable fabric has limitations:
Sharp Objects: Can be punctured by knives, glass, or pet claws.
Use on clean, flat surfaces.
Extreme Heat: Prolonged exposure to high heat (e.g., direct sunlight on dark surfaces) can soften or warp the material.
Poor Storage: Folding while damp or storing in hot areas can lead to mold or glue degradation.
Aging: Over time, UV exposure and oxidation can make the PVC brittle—typically after 3–5 years.
To maximize strength and lifespan:
Always patch small holes promptly with PVC repair kits.
Clean with mild soap and water.
Store dry, cool, and away from sunlight.
Yes, PVC inflatable fabric is strong—especially when engineered with a reinforced scrim and quality coatings. Its combination of tensile strength, tear resistance, durability, and environmental resilience makes it one of the most reliable materials for inflatable products. While not indestructible, it offers an excellent balance of performance, safety, and affordability for both consumer and commercial use. With proper handling and maintenance, PVC inflatable fabric can remain strong and functional for many years, proving its value across countless real-world applications. For most users, it is more than strong enough to meet their needs.


 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español