Understanding Waterproof Performance in Flexible Plastic Sheets
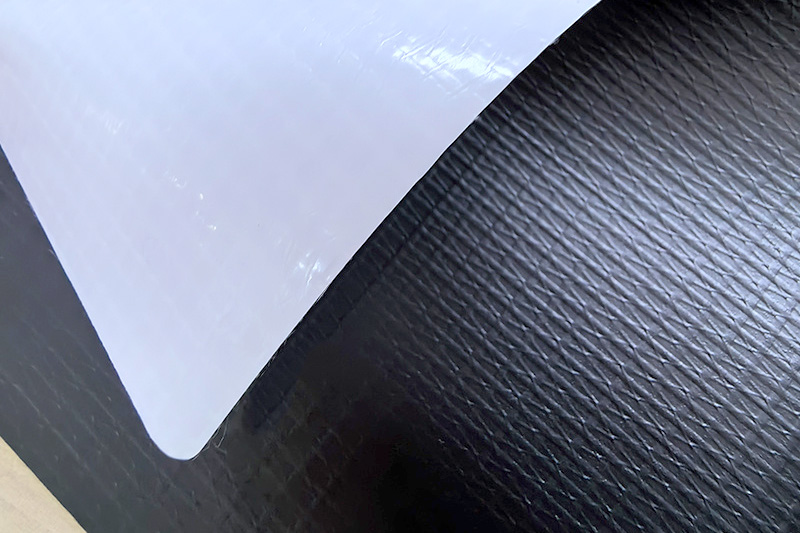
Waterproof performance is one of the most important functional properties of flexible plastic sheet material. In many applications, these sheets are expected to block water, resist moisture penetration, and maintain structural integrity even after long-term exposure to wet environments. However, not all flexible plastic sheets offer the same level of waterproofing, and their effectiveness depends on material type, thickness, and manufacturing process.
Unlike rigid plastic panels, flexible plastic sheets must maintain water resistance while bending, folding, or stretching. This makes material formulation and surface integrity critical factors in determining how waterproof the sheet truly is in real-world use.
What “Waterproof” Means for Flexible Plastic Materials
In practical terms, a waterproof flexible plastic sheet material prevents liquid water from passing through its surface under normal use conditions. This differs from water-resistant materials, which may repel water initially but allow slow moisture penetration over time.
For flexible plastic sheets, waterproofing is typically achieved through low water absorption, dense polymer structure, and absence of pores or microcracks. True waterproof sheets can be submerged in water without allowing leakage, provided seams and edges are properly sealed.
Common Flexible Plastic Sheet Materials and Their Waterproof Levels
Different plastic polymers exhibit varying degrees of water impermeability. Understanding these differences helps users select the most suitable flexible plastic sheet material for wet or humid applications.
| Material Type | Water Absorption | Waterproof Level | Typical Applications |
| PVC Sheet | Very Low | High | Curtains, covers, flooring |
| PE Sheet | Extremely Low | Very High | Liners, packaging, barriers |
| PU Sheet | Low | High | Protective films, coatings |
| TPU Sheet | Low | High | Outdoor gear, medical uses |
Thickness and Its Impact on Waterproofing
Thickness plays a direct role in how waterproof a flexible plastic sheet material is. Thicker sheets provide a longer diffusion path for moisture, reducing the chance of water penetration under pressure or prolonged exposure.
However, increasing thickness may reduce flexibility. Selecting the optimal balance between waterproof performance and flexibility is essential, especially in applications such as foldable covers or roll-up barriers.
Seams, Edges, and Installation Factors
Even when the base material is fully waterproof, overall system performance depends heavily on seams, joints, and edges. Poorly sealed edges can allow water ingress, undermining the sheet’s inherent waterproof properties.
Heat welding, solvent bonding, and adhesive sealing are commonly used methods to maintain waterproof integrity in flexible plastic sheets. Proper installation techniques are just as important as material selection.
Resistance to Long-Term Moisture Exposure
Flexible plastic sheet materials generally perform well in long-term moisture exposure scenarios. They do not rot, swell, or support mold growth in the way that organic materials do. This makes them suitable for damp environments such as basements, bathrooms, and outdoor enclosures.
However, prolonged exposure to standing water combined with UV radiation or high temperatures can accelerate material aging. UV-stabilized formulations help maintain waterproof performance in outdoor applications.
Waterproof Performance Under Movement and Stress
A key advantage of flexible plastic sheets is their ability to maintain waterproofing even when bent or flexed. Materials such as TPU and PE can endure repeated movement without developing cracks that allow water penetration.
Lower-quality materials may develop microfractures over time, especially under cold temperatures or excessive mechanical stress. Selecting sheets designed for dynamic use is essential in applications involving frequent motion.
Common Waterproof Applications of Flexible Plastic Sheets
Because of their excellent waterproof characteristics, flexible plastic sheet materials are widely used across multiple industries. Their adaptability allows them to function as both protective barriers and functional components.
- Protective covers and tarpaulins
- Waterproof curtains and partitions
- Liners for containers and ponds
- Moisture barriers in construction
How to Choose the Right Waterproof Sheet
Choosing a truly waterproof flexible plastic sheet material involves more than selecting a plastic type. Users must consider environmental conditions, mechanical stress, exposure duration, and installation method.
For static indoor applications, PVC or PU sheets may be sufficient. For outdoor or high-movement applications, PE or TPU sheets with UV stabilization provide superior long-term waterproof reliability.
Conclusion: Evaluating Real-World Waterproof Performance
Flexible plastic sheet material can be highly waterproof when the correct polymer, thickness, and installation method are chosen. Materials such as PE, PVC, and TPU offer excellent resistance to water penetration, even in demanding environments.
By understanding how material properties, thickness, and real-world conditions interact, users can confidently select flexible plastic sheets that provide reliable, long-lasting waterproof performance.


 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español