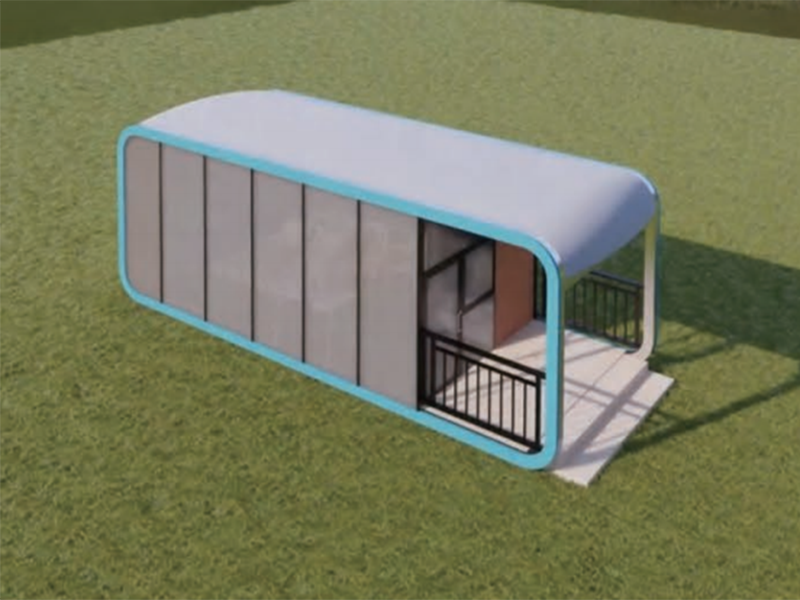
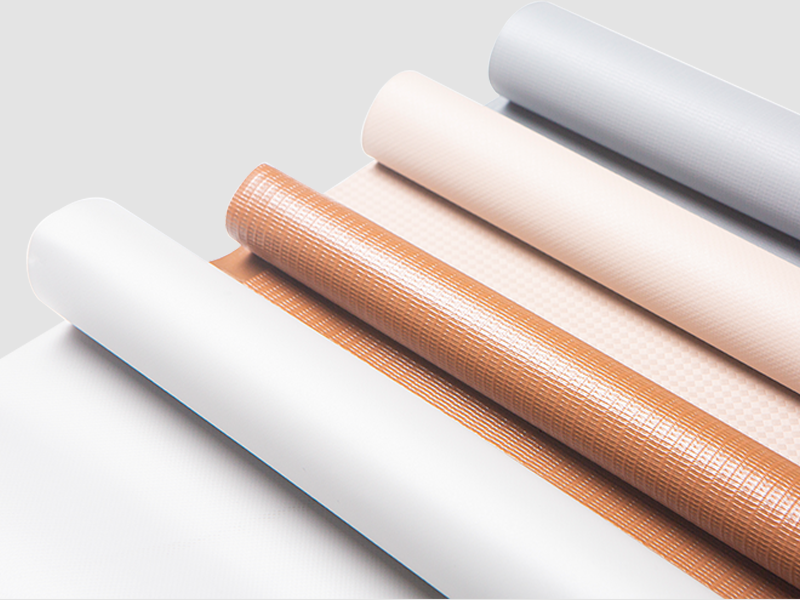
Introduction to Flex Material
Flex materials, often referred to as flexible or elastic materials, are widely used in industries ranging from electronics to automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods. Their unique ability to bend, stretch, or conform to shapes while maintaining structural integrity makes them highly versatile. Among the key properties that define flex materials are their waterproof and heat-resistant capabilities, which determine their suitability for specific applications.
The combination of polymer type, material thickness, and surface treatment significantly influences performance, allowing designers to select materials that meet environmental and operational requirements.
Material Composition and Types
Flex materials are primarily composed of polymers such as silicone, polyurethane (PU), thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), and polyethylene (PE). Each type exhibits different levels of waterproofing, heat resistance, and mechanical flexibility. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the appropriate material for a given application.
Silicone Flex Material
Silicone-based flex materials are renowned for their high heat resistance, maintaining performance at temperatures ranging from -60°C to 250°C. They are also inherently waterproof due to their non-porous structure, making them ideal for gaskets, seals, kitchenware, and medical devices exposed to moisture or extreme temperatures.
Polyurethane (PU) Flex Material
PU-based flex materials offer excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance. While moderately heat-resistant (typically up to 120°C), they are highly water-resistant, especially when treated with hydrophobic coatings. PU flex materials are commonly used in flexible hoses, protective covers, and wearable devices.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
TPE materials combine the elasticity of rubber with the processability of plastics. They exhibit good waterproof properties and moderate heat resistance, typically around 100°C to 150°C, depending on the formulation. TPE is often used in cable insulation, protective seals, and flexible connectors.
Waterproof Properties of Flex Materials
Waterproof performance is a critical factor for flex materials used in outdoor or liquid-exposed environments. The non-porous nature of polymers, combined with surface treatments or coatings, prevents water penetration, maintaining mechanical integrity and electrical insulation.
Factors Affecting Waterproof Performance
- Polymer type: Silicone and PE are naturally waterproof, while TPE and PU may require coatings.
- Thickness: Thicker materials generally provide better waterproofing.
- Surface treatment: Hydrophobic or UV-resistant coatings improve resistance to moisture and degradation.
Heat Resistance Performance
Heat resistance determines the maximum temperature a flex material can withstand without losing elasticity, deforming, or breaking down chemically. Silicone leads in high-temperature performance, while PU and TPE offer moderate resistance. Proper material selection ensures functionality in high-heat environments like automotive engines, industrial machinery, or electronic housings.
Factors Affecting Heat Resistance
- Polymer chemistry: Cross-linking in silicone enhances thermal stability.
- Fillers and additives: Mineral fillers improve heat endurance in PU or TPE materials.
- Environmental exposure: Continuous UV or direct flame may reduce heat resistance over time.
Comparison Table: Waterproof and Heat-Resistant Flex Materials
| Material | Waterproof | Max Heat Resistance | Common Applications |
| Silicone | Excellent | 250°C | Seals, Gaskets, Kitchenware |
| PU | High | 120°C | Hoses, Protective Covers |
| TPE | Moderate to High | 150°C | Cable Insulation, Flexible Connectors |
| PE | Excellent | 80°C | Protective Films, Covers |
Applications of Waterproof and Heat-Resistant Flex Materials
Waterproof and heat-resistant flex materials are used in diverse applications requiring durability and environmental protection. Examples include:
- Automotive seals, gaskets, and engine components exposed to heat and moisture.
- Protective covers for electronic devices, preventing water ingress.
- Medical equipment components requiring sterilization at high temperatures.
- Outdoor installations, wearable devices, and flexible tubing in harsh environments.
Maintenance and Handling
Maintaining waterproof and heat-resistant flex materials involves avoiding prolonged exposure to chemicals, direct flame, or extreme UV light. Gentle cleaning, proper storage, and correct installation help maintain mechanical integrity, color stability, and waterproof performance over time.
Conclusion: Performance Considerations
Flex materials offer a combination of waterproofing and heat resistance that makes them suitable for demanding industrial, automotive, medical, and consumer applications. Silicone provides the highest heat and water resistance, PU and TPE offer moderate to high protection with flexibility, and PE offers excellent waterproofing with basic heat tolerance. Selecting the right flex material based on environmental conditions and operational requirements ensures durability, safety, and long-term performance.


 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español